formal charge on co2|formal charge of c : Pilipinas With formal charge, the electrons in each covalent bond are assumed to be split exactly evenly between the two atoms in the bond (hence the dividing by two in the .
Watch Pinay Nalasing porn videos for free, here on Pornhub.com. Discover the growing collection of high quality Most Relevant XXX movies and clips. No other sex tube is more popular and features more Pinay Nalasing scenes than Pornhub! Browse through our impressive selection of porn videos in HD quality on any device you own.
PH0 · formal charge of c
PH1 · carbon dioxide formal charge
PH2 · Iba pa
Specialties: Baber Auto Repair provides quality car care in Roseville, MN. We are a family-owned business delivering honest and professional automotive repair and auto maintenance services to the people of Roseville and surrounding areas. The technicians at Baber Auto Repair employ today's latest automotive technology and are equipped to .PRC Resolution No. 2020-1267 (s.2020) According to PRC Resolution No. 2020-1267 (s.2020), which was recently issued: Board exam repeater examinees after June 2018 will no longer be expected to directly file their applications and submit copies of their requirements such as their NSO Birth Certificates, Marriage Certificates (for female .
formal charge on co2*******The formula for formal charge: F C = V-N-B 2. Here, F C is the formal charge, V is number of valence electrons, N is number of nonbonding valence electrons and B is total number of electrons shared in bonds. Formal charge on Carbon atom in CO 2. In carbon dioxide . Since carbon has 4 valence electrons, its formal charge will be zero. The same is true for both oxygen atoms. Both of them form 2 bonds, which means they get 2 . In order to calculate the formal charges for CO2 we'll use the equation Formal charge = [# of valence electrons] - [nonbonding val electrons] - [bonding . The formal charge on carbon is equal to the number of valence electrons that carbon is supposed to have, which we know is four, and from that we subtract the number of valence electrons that carbon actually has in our drawing.formal charge on co2 formal charge of c The formal charge on carbon is equal to the number of valence electrons that carbon is supposed to have, which we know is four, and from that we subtract the number of valence electrons that carbon actually has in our drawing.Formal charge is assigned to an atom in a molecule by assuming that electrons in all chemical bonds are shared equally between atoms, regardless of relative . With formal charge, the electrons in each covalent bond are assumed to be split exactly evenly between the two atoms in the bond (hence the dividing by two in the .Formal charge are a way of keeping track of where the electrons an atom donates to a Lewis dot structure are placed. The sum of the formal charges equals the charge of the .
The formal charge of an atom in a molecule is the charge that would reside on the atom if all of the bonding electrons were shared equally.
A formal charge is a charge assigned to an atom in a molecule, assuming that all electrons in the chemical bonds are shared equally between the atoms. This assumption .We can double-check formal charge calculations by determining the sum of the formal charges for the whole structure. The sum of the formal charges of all atoms in a .
The formal charges on the atoms in the \(\ce{NH4^{+}}\) ion are thus. Adding together the formal charges on the atoms should give us the total charge on the molecule or ion. In this case, the sum .Formal charge are a way of keeping track of where the electrons an atom donates to a Lewis dot structure are placed. The sum of the formal charges equals the charge of the structure. . where one of the dots on the right side is near a carbon, meaning one of the electrons nitrogen donated is near the carbon. Exercise \(\PageIndex{1}\) Which .
formal charge = # valence shell electrons (free atom) − # lone pair electrons − 1 2 # bonding electrons. We can double-check formal charge calculations by determining the sum of the formal charges for the .What is a formal charge. Learn its equation, along with a few examples and diagrams. Also, learn how to find the formal charge. Chemistry Learner It's all about Chemistry. . Therefore, formal charge on carbon in CO 2 is given by, q f = 4 – 0 – 8/2 = 0. For oxygen, V = 6, N = 4, B = 4.
Using Equation 2.3.1 to calculate the formal charge on hydrogen, we obtain. Formal Charge of H = (1 valence e-) - (0 lone pair e-) - (1/2 x 2 bond pair e-) = 0. The sum of the formal charges of each atom must be equal to the overall charge of the molecule or ion.
In each of them, the formal charge on the center carbon is 0, the double bonded oxygen is 0, and the two single bonded oxygens are each -1. See if you can calculate these yourself correctly! Note that as discussed above, 0 + 0 + (-1) + (-1) adds up to -2, which is the overall charge on the ion. .formal charge on co2 Formal charge. The formal charge of an atom in a molecule is the charge that would reside on the atom if all of the bonding electrons were shared equally. We can calculate an atom's formal charge using the equation FC = VE - [LPE - ½ (BE)], where VE = the number of valence electrons on the free atom, LPE = the number of lone pair .formal charge of c Formal charge. The formal charge of an atom in a molecule is the charge that would reside on the atom if all of the bonding electrons were shared equally. We can calculate an atom's formal charge using the equation FC = VE - [LPE - ½ (BE)], where VE = the number of valence electrons on the free atom, LPE = the number of lone pair .
In order to calculate the formal charges for CO3 2- we'll use the equation:Formal charge = [# of valence electrons] - [nonbonding val electrons] - [bonding e.
formal charge on carbon = (4 valence electron on isolated atom) - (0 nonbonding electrons) - (½ x 8 bonding electrons) = 4 - 0 - 4 = 0. So the formal charge on carbon is zero. For each of the hydrogens in methanol, we also get a formal charge of zero: formal charge on hydrogen = (1 valence electron on isolated atom) - (0 .Calculate the formal charge for each atom in the carbon monoxide molecule: Answer: C −1, O +1. Example 7.7. Calculating Formal Charge from Lewis Structures Assign formal charges to each atom in the interhalogen molecule BrCl 3. Solution. Step 1.The formal charges on the atoms in the NH+4 NH 4 + ion are thus. Adding together the formal charges on the atoms should give us the total charge on the molecule or ion. In this case, the sum of the formal charges is 0 + 1 + 0 + 0 + 0 = 1+, which is the same as the total charge of the ammonium polyatomic ion.Thus, we calculate formal charge as follows: formal charge = # valence shell electrons (free atom) − # lone pair electrons − 1 2 # bonding electrons (10.7.1) (10.7.1) formal charge = # valence shell electrons (free atom) − # lone pair electrons − 1 2 # bonding electrons. We can double-check formal charge calculations by determining the . Assign formal charge. To calculate the formal charges on the atoms in CO 2, use the formula: Formal charge = valence electrons – nonbonding electrons – ½ bonding electrons. For the carbon atom, the formal charge is calculated as 4 – 0 – ½ (4) = +2, while for each oxygen atom, the formal charge is 6 – 6 – ½ (2) = -1.Formal charge can help us to understand the behavior of carbon monoxide, CO C O. When exposed to transition metal cations such as the iron in hemoglobin ( Fe 2+), the carbon is attracted to and binds to the metal. In the case of hemoglobin, because the carbon monoxide binds very strongly to the iron, the CO blocks the position where .
Formal charge on the Carbon atom = 4 – 0 – 8/2 = 0. ∴ The formal charge on the central Carbon (C) atom in CO2 is 0. For double-bonded Oxygen atom. Valence electrons of Oxygen = It is present in Group VI A = 6 valence electrons. Bonding electrons around Oxygen = 1 double bond = 4 electrons. Non-bonding electrons on .
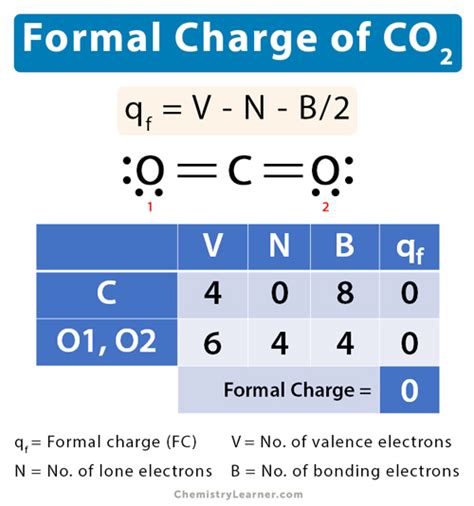
The carbon dioxide Lewis structure and formal charge.(Chem 1090 Lewis 6a) In order to calculate the formal charges for CO32- we'll use the equationFormal charge = [# of valence electrons] - [nonbonding val electrons] - [bonding e.
Carbon double bonded to both oxygen atoms (carbon = 0, oxygens = 0, total formal charge =0). Even though all three structures gave us a total charge of zero, the final structure is the superior one because there are no charges in the molecule at all.
UnionBank Credit Cards | Smart. Shop for gadgets including the iPhone 15 or pay for your device cash-out with your UnionBank Credit Card.
formal charge on co2|formal charge of c